A Smarter Way to Screen for Drug Candidates
In the quest to develop the ideal drug candidate, performing developability assessment early can prevent costly missteps.
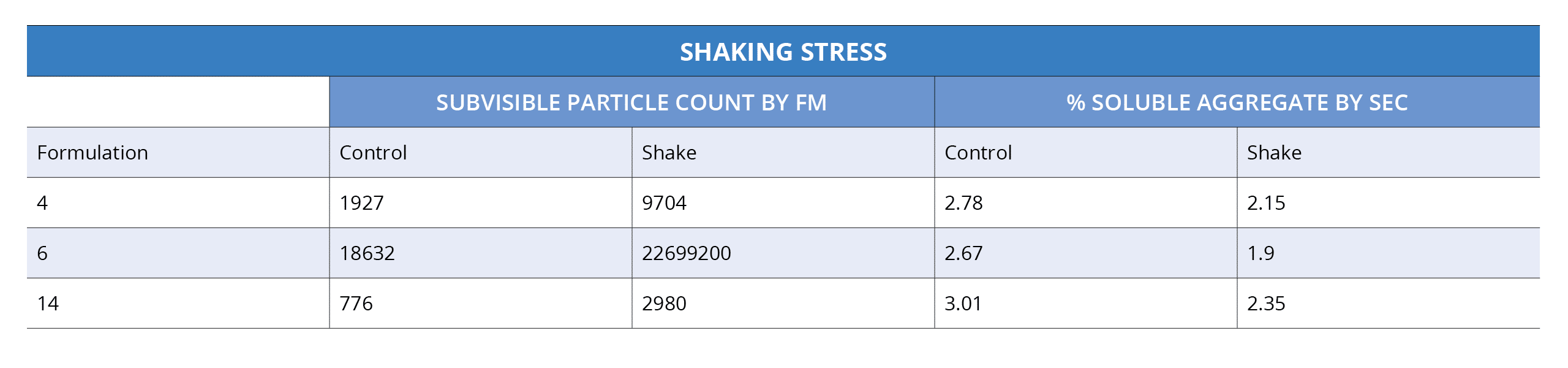
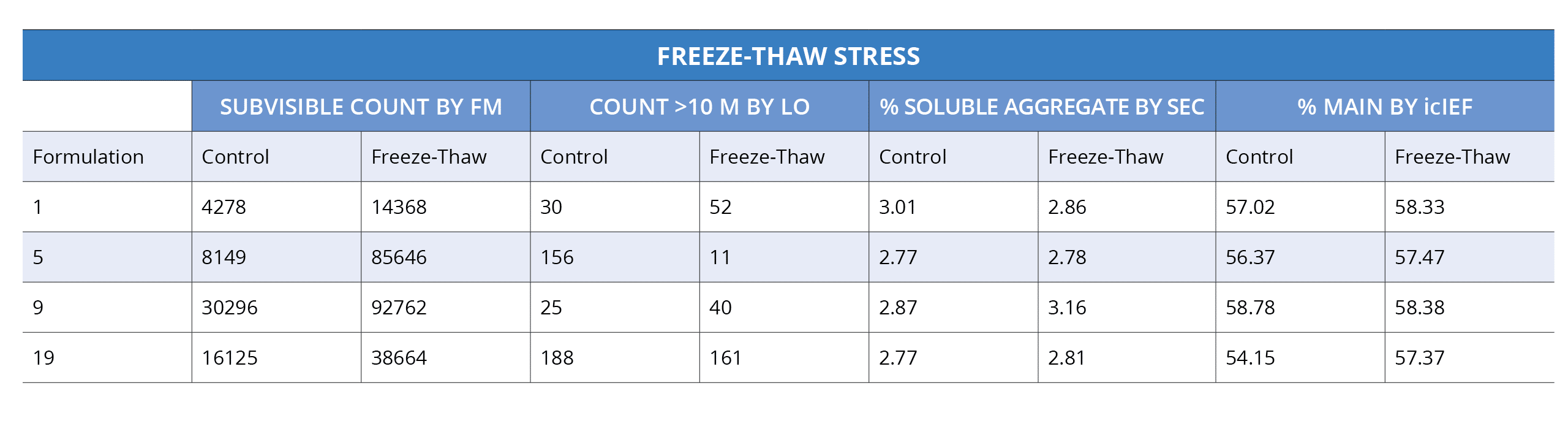
Unfortunately, traditional particle analysis methods require more volume than may be available during early research stages. In addition, some low volume techniques don’t predict subvisible particles, which fall into a unique size range: too big for DLS and SEC, too small for the eye to see.
That's why we developed Aura PTx for smarter screening throughout your entire development process. With this innovative particle analyzer, you’ll be able to narrow down potential candidates quickly and accurately, from discovery all the way to downstream.
Why Use Aura for Protein Developability?
Because you can achieve so much more insight with much less material:
- Detect and characterize particles not measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS) or size exclusion chromatography (SEC)
- Preserve sample using as little as 5 μL per test for early candidate screening and selection
- Identify critical quality attributes (CQA) early and often
- Quickly screen a wide range of conditions with our 96-well format
- Obtain detailed information on particles that other methods can’t deliver, including size, morphology, count, and distribution
- Move quickly with an analysis time of about 1 minute per sample
- Evaluate a wide range of particle sizes, measuring 1 μm to 5 mm with high reproducibility
- Achieve high sensitivity because particles are imaged without the interference of buffer or matrix
Identify Optimal Biologic Candidates:
Low Volume, Early Stage Developability with Aura PTx
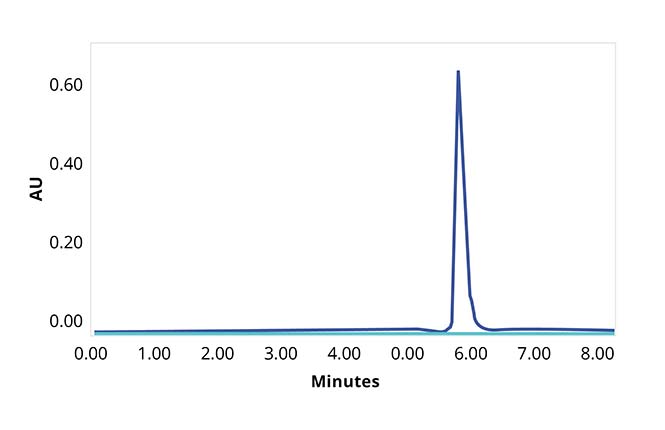
Aura PTx is transforming the sample volume limited developability assessment stage by enabling subvisible particle characterization — the most
important critical quality attribute (CQA). Its high throughput, low volume modality enables high-level ranking decision making and reveals the most granular insights into particle formation and stability on a single platform.
Get the Full Picture of Protein Stability
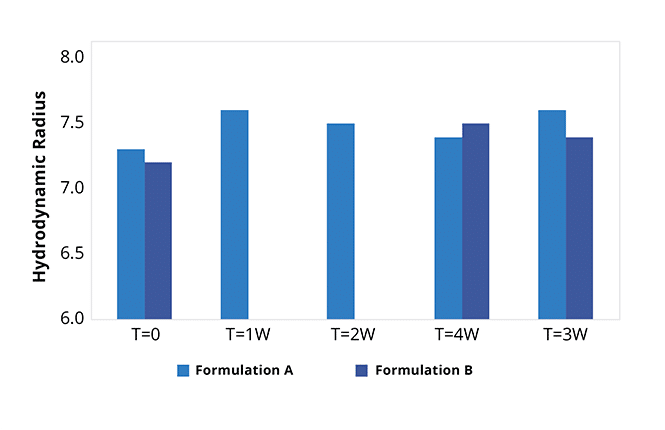
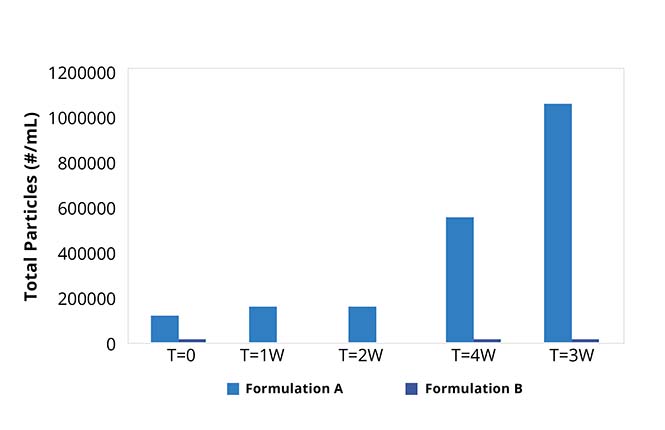
During the critical candidate selection stage, it's important to understand a protein's behavior. Properties like aggregation, stability, and hydrophobicity must be taken into account, but using limited methods such as SEC or DLS only captures part of the story.
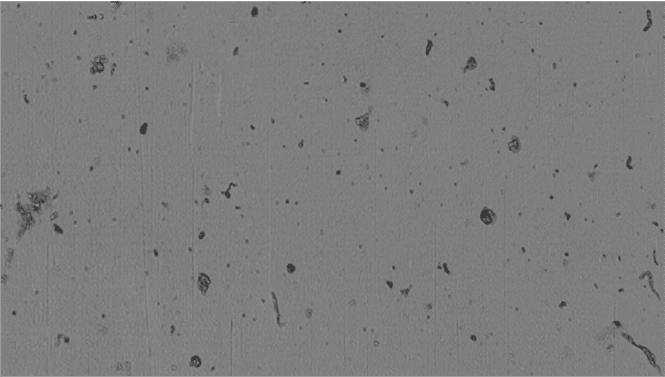
To completely evaluate proteins for antibody developability assessment and pre-formulations in detail, we need to go even beyond what these traditional techniques offer—probing down into the "subvisible" range can reveal details that would otherwise remain hidden.
Because automated analysis with Backgrounded Membrane Microscopy (BMI) is fast and only needs as little as 5 uL per sample, it can be used early on in your developability assessment and preformulation studies to detect larger, insoluble aggregates.
This measurement completes the stability picture, reducing risk and letting you make more educated decisions about which candidates to move into development.