Gain Critical Insights For Better Decision Making
With the ability to deliver comprehensive particle counting, identification, and characterization on as little as 5 µL of sample, the Aura family of instruments give gene therapy developers and manufacturers critical information while preserving precious samples early in development.
Innovative Technology Enables Early Candidate Characterization and Selection
Unlike flow imaging, which requires milliliters of sample, Aura systems can quickly and easily characterize viral vector and other types of gene therapies with just 5µL of sample. This is due to analyzing samples via membrane microscopy which requires meniscal amounts while maintaining 100% sampling efficiency.
Begin candidate screening and selection much earlier in development providing the confidence needed when commercializing your gene therapy.
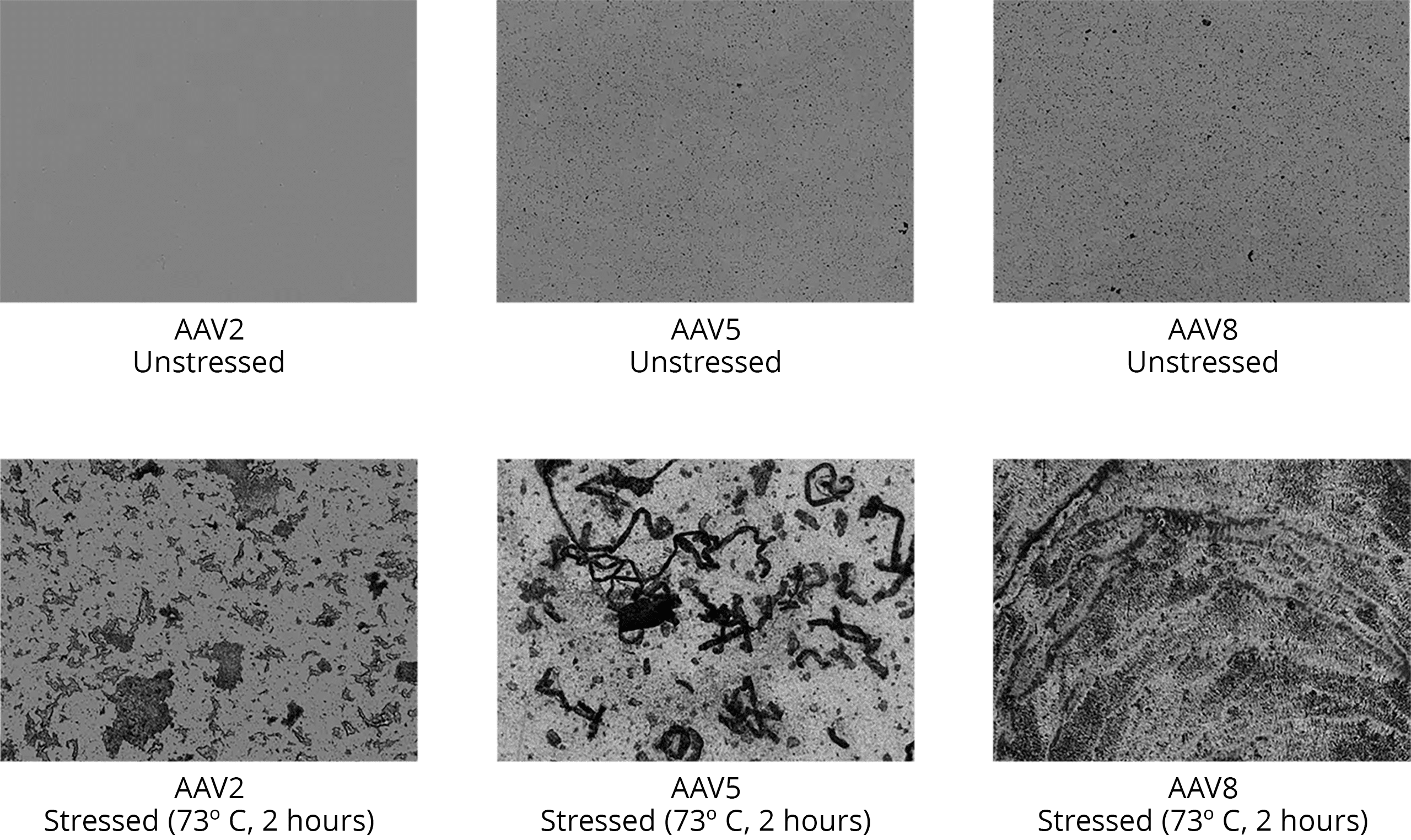
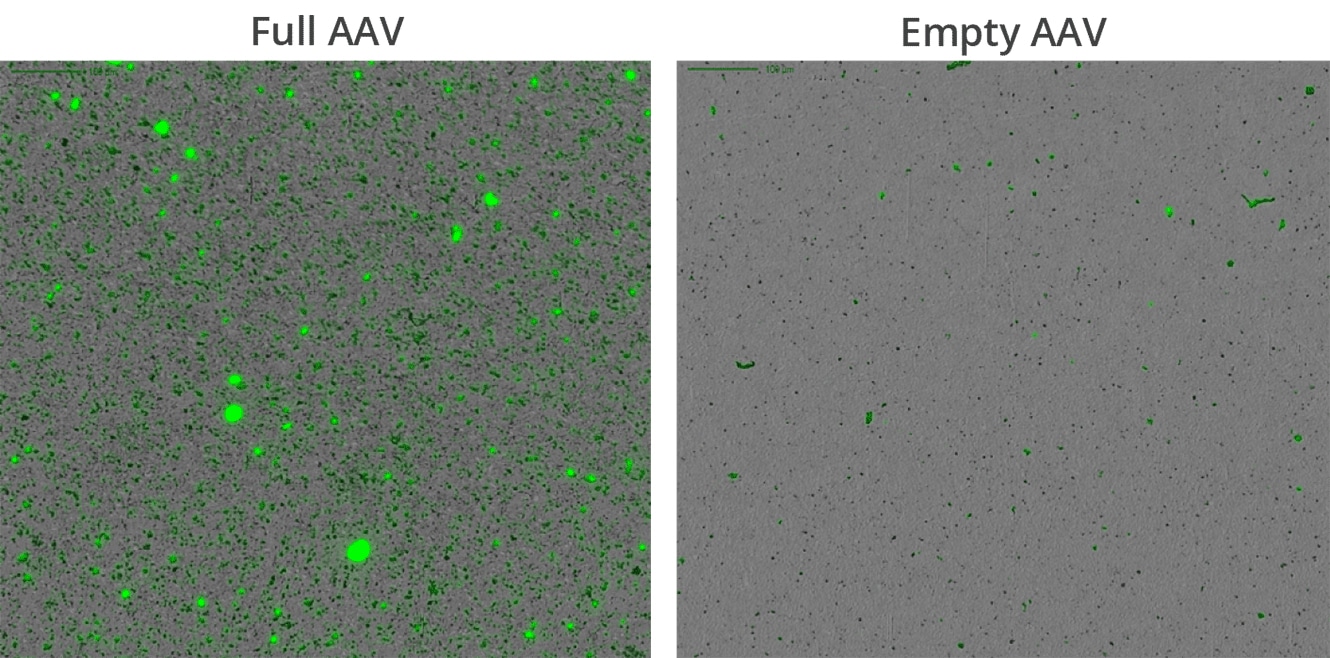
Determine Root Cause of Viral Vector Instability
Leveraging Fluorescence Membrane Microscopy (FMM), interrogate your drug products to determine what’s causing aggregation and instability.
It’s widely known and accepted that DNA leakage from full but comprised AAV capsids promote aggregation. At ultra-low volumes, Aura GT enables comprehensive product characterization without wasting costly precious samples.
Frequently Asked Questions
Gene therapy manufacturing faces various challenges, including:
- Scalability: Gene therapy manufacturing processes need to be scalable to meet increasing demand and accommodate large-scale production.
- Viral Vector Production: Producing viral vectors (such as AAV or lentivirus) used for gene delivery in large quantities and with high purity is challenging and time-consuming.
- Regulatory Compliance: Gene therapy manufacturing processes must comply with stringent regulatory requirements to ensure product safety, efficacy, and quality.
- Cost: Gene therapy manufacturing involves complex and costly processes, including cell culture, purification, and quality control testing, which can result in high manufacturing costs.
- Technology Transfer: Transferring gene therapy manufacturing processes from research to commercial-scale production while maintaining consistency and quality presents logistical and technical challenges.
Efforts are underway to address these challenges through advancements in technology, process optimization, and regulatory support to accelerate the development and commercialization of gene therapy products.
Viral vector vaccines are manufactured using a multistep process that typically involves:
- Selection and Engineering of Viral Vector: A suitable viral vector, such as adenovirus or AAV, is selected or engineered to carry the genetic material encoding the antigen of interest.
- Cell Culture and Viral Vector Production: The viral vector is produced using mammalian cell culture systems, such as HEK293 cells, or other suitable host cells. The cells are infected with the viral vector, and the vector particles are harvested and purified.
- Antigen Insertion: The genetic material encoding the antigen of interest is inserted into the viral vector genome using recombinant DNA technology.
- Vaccine Formulation: The purified viral vector particles containing the antigen are formulated into the final vaccine product, which may include adjuvants or stabilizers to enhance immune response and stability.
- Quality Control Testing: The vaccine undergoes rigorous quality control testing to ensure safety, purity, potency, and stability before release for distribution.
Viral vector vaccines offer promising approaches for vaccine development against various infectious diseases and have been utilized in COVID-19 vaccines, Ebola vaccines, and others.
AAV (Adeno-associated virus) production typically involves several days to weeks to complete, depending on various factors such as the production scale, cell culture conditions, and purification process. The production timeline includes cell culture and transfection to generate AAV particles, followed by purification and concentration steps to isolate the viral vectors from cellular components and contaminants. Advanced manufacturing technologies and process optimization strategies are being implemented to accelerate AAV production and improve efficiency.